
A stress fracture is a tiny hairline fracture that occurs slowly over time. We suggest serious consideration be given to the method herein as a form of primary treatment of the early chronic Jones' fracture without intramedullary sclerosis. Jones fractures are caused by repetitive stress (stress fracture) or trauma, such as dropping something heavy on the foot. Our data indicate that nonoperative treatment of early chronic or subacute fractures without intramedullary sclerosis can compare favorably with surgical treatment procedures reported in other studies in returning athletes to play postinjury. All competitive athletes returned to their preinjury level of competition at an average of 12 weeks following initiation of treatment. Jones fracture, on the other hand, involves the shaft of the fifth metatarsal and has a propensity to not heal. Due to conflicting results, the most appropriate treatment method remains unclear. Some studies have assessed immediate weight bearing following a Jones fracture. This can occur from overuse, playing sports, dancing, or a slip-and-fall accident. Classically, treatment consists of weight bearing restrictions in a cast or surgical fixation. Jones fractures are caused by sudden force on the outside of the foot when twisted, usually with the heel off the ground. Prevention FAQs Summary The fifth metatarsal is the long bone on the outer edge of the foot that connects to your smallest toe, sometimes called the pinky toe. Mean clinical and radiographic union of chronic fractures was 9.4 weeks acute fractures, 22 weeks. Treatment A Jones fracture is a break in the long bone outside the foot ( fifth metatarsal) that connects to the pinky toe. Treatment consisted of a short leg nonweightbearing cast until radiographic and clinical healing occurred, followed by 6 weeks of limited activity. In this group, competitive athletes sustained chronic fractures, while acute fractures occurred in nonathletes. Sir Robert Jones, in 1902, described a transverse fracture of the proximal diaphysis of the fifth metatarsal, which he treated conservatively with good. The cases were categorized as acute or chronic by clinical history and radiographic appearance. A retrospective study of nine patients with 10 Jones' fractures was completed.
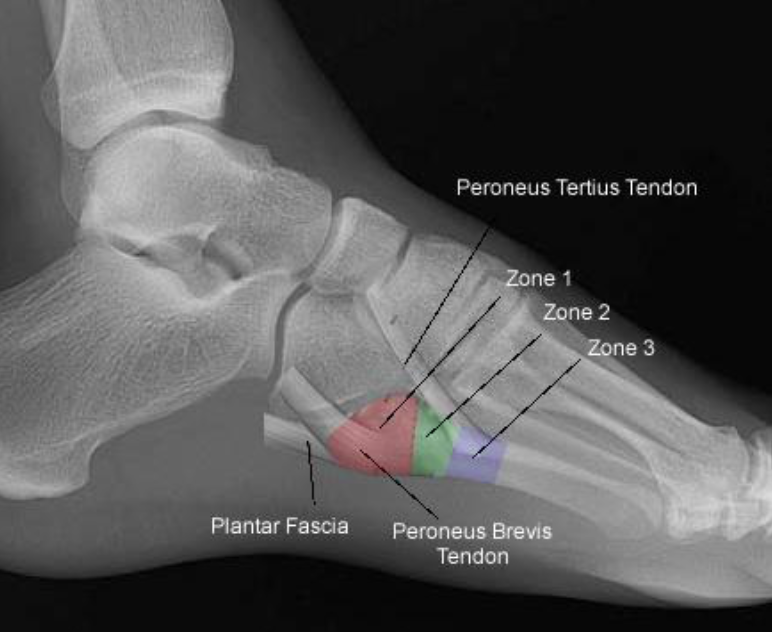
The purpose of this study was to determine if nonoperative treatment could be used effectively in treating these fractures. Controversy exists concerning operative versus nonoperative primary treatment especially in athletes.

You will need to wear a cast or boot on your foot and use crutches until the bone has healed and can bear weight again. These fractures will sometimes heal on their own, but may take months to heal without surgery. Since that time, classification into acute and chronic categories by several authors has been proposed and most agree with the relatively high incidence of non-union. Jones fracture surgery may be needed to align the bone and help with healing. Sir Robert Jones, in 1902, described a transverse fracture of the proximal diaphysis of the fifth metatarsal, which he treated conservatively with good results.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
